Wish SUS Cost Less? Survey Says Your Peers Do, Too
By Ioanna Deni, Bioplan Associates Inc.

The COVID-19 pandemic was a watershed moment for the biomanufacturing industry, not only in terms of the global demand for vaccines and therapeutics but also in the challenges it presented to the suppliers of critical materials and equipment. This experience led to a significant shift in the industry's priorities, with a clear focus on solutions that could enhance operational efficiency and reduce manufacturing costs — demands that suppliers are now expected to meet.
According to the BioPlan Associates 21st Annual Report,1 the single most important new product development area that suppliers need to focus their efforts on is low-cost single-use systems (SUS), with 32.3% of biomanufacturing professionals reporting it in 2024.
Costs of SUS were also an issue pre-pandemic. But costs rose substantially due to supply challenges during COVID. As a result, demand for lower-cost SUS has taken the top spot on the industry’s wish list. By comparison, improvements in automation moved to second place — despite the industry’s long-term interest in automating processes.
In 2021, as the industry was adjusting to the COVID-19 pandemic, automation emerged as a critical area of innovation, with 31.3% of biomanufacturing professionals urging suppliers to develop automated solutions for the first time. In 2024, automation remains a priority, with 28.6% of professionals still emphasizing its importance (Figure 1). This persistent trend underscores the growing expectation that suppliers will deliver these solutions to meet the evolving needs of biomanufacturing in a post-pandemic landscape.
Figure 1: Most important new product development suppliers need to focus on in 2024
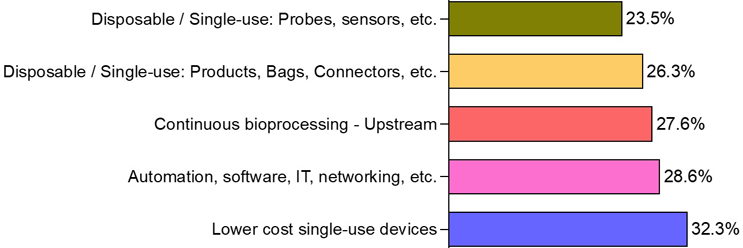
Source: 21st Annual Report and Survey of Biopharmaceutical Manufacturing Capacity, 2024, BioPlan Associates, Inc. Rockville, MD
Great Majority Of Manufacturers Have Incorporated Some Form Of SUS
SUS have become a cornerstone in modern biomanufacturing, offering a multitude of advantages that have driven their widespread adoption across the industry. This year, 87% of responding manufacturing facilities have incorporated some form of SUS. For example, single-use bioreactors are used by over 80% of biomanufacturing facilities.1 One of the most significant benefits of SUS is the reduction in cleaning and validation requirements. Unlike traditional stainless-steel systems, SUS:
- eliminates the need for extensive cleaning protocols, and
- reduces the associated risk of cross-contamination.
This not only lowers the burden on facility operations but also significantly reduces the time and resources needed for validation, as these tasks are largely handled by the SUS suppliers. While validation tasks for the end user are reduced, they are not entirely eliminated, offering a balance between convenience and compliance.
SUS also allows:
- a lower up-front capital investment compared to stainless steel systems,
- operational efficiency, which translates to decreased staffing requirements, and
- flexibility, allowing for rapid turnover and significantly shorter lead times in getting a facility or process line up and running.
This adaptability is particularly valuable in a dynamic industry where speed to market can be a critical competitive advantage. Moreover, the evolution of SUS has made entirely single-use processes a reality, enabling cost-competitive large-scale commercial manufacturing. This includes the practice of scaling-out by running multiple single-use systems in parallel, further enhancing production capabilities. Even older, more conventionally built stainless-steel facilities are recognizing the benefits of SUS and are moving toward hybrid models. These facilities are modifying their existing infrastructure to optimally incorporate SUS for production, blending the reliability of traditional systems with the innovative advantages of single-use technologies.
Cost Of Product Persistently Causing Dissatisfaction For 4 Out Of 5 Professionals
Despite the clear benefits and successful adoption of SUS, there remains a significant gap in customer satisfaction concerning the cost of these systems. While nearly 80% of biomanufacturers rate cost management as a crucial factor, only 33% express satisfaction with the cost of SUS provided by their vendors (Figure 2). This gap underscores a persistent challenge that vendors are being asked to address to meet the industry's evolving demands.
Figure 2: Selected data — importance of single-use product attributes vs. level of vendor satisfaction, data from 2024
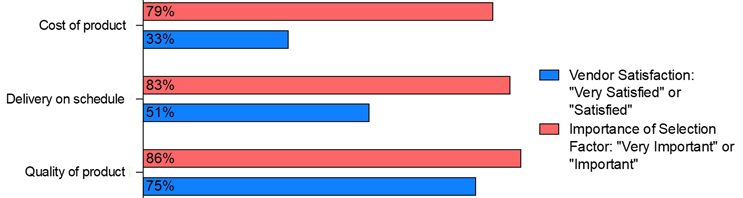
Source: 21st Annual Report and Survey of Biopharmaceutical Manufacturing Capacity, 2024, BioPlan Associates, Inc. Rockville, MD
To bridge this gap, vendors may need to reevaluate their cost structures and explore new strategies to offer more value to their customers.
Potential areas for cost reduction include:
- Streamlining manufacturing processes: Implement more efficient production techniques to reduce costs without compromising product quality.
- Leveraging economies of scale: Expand production capacity to benefit from lower per-unit costs as demand for SUS continues to grow.
- Innovative pricing models: Explore alternative pricing strategies, such as subscription-based models or tiered pricing, to provide more value to customers.
These approaches could make SUS more accessible and financially viable for a broader range of biomanufacturers (especially emerging regions or niche manufacturers). In addition to cost concerns, the issue of sustainability within the SUS sector has gained attention. The biopharmaceutical industry is increasingly focused on reducing its carbon footprint and improving the sustainability of disposable materials.
Currently, only 37% of biomanufacturers report satisfaction with their vendors' recycling programs for SUS, indicating significant room for improvement. A number of organizations, such as the ISPE,2 have established communities of practice to address such issues.
Vendors are responding by developing technologies that enhance the reusability and recyclability of SUS. However, challenges such as contamination risks and the complexities of decontamination processes, coupled with a limited recycling infrastructure, make this a difficult task. Despite these obstacles, the relatively small gap between satisfaction with vendors' recycling programs (37%) and the importance of sustainability (48%) suggests that biomanufacturers appreciate the current solutions and are optimistic that vendors will continue to innovate in this area.
A Third Of Biomanufacturing To Adopt Automated Systems
Automation has become an integral part of the biomanufacturing industry, driving efficiency, consistency, and scalability in production processes. Over the past 15 years, the adoption of automated batch control systems for bioreactors has seen significant growth, reflecting the industry's increasing reliance on technology to meet the demands of modern bioprocessing. In 2009, only about 9% of facilities planned to adopt automated batch control systems. By 2024, this number has risen to nearly 30%, underscoring the critical role that automation now plays in the industry. These roles include:
- Ensuring consistent and reliable production: Automation minimizes human error, ensuring that biomanufacturing processes are consistent and reliable. This is crucial in maintaining product quality and meeting regulatory standards.
- Streamlining production processes: By automating batch control, facilities can reduce cycle times and increase throughput, leading to more efficient production and faster time-to-market for new therapies.
- Providing real-time monitoring and control: Automation enables real-time monitoring and control of critical process parameters, allowing for immediate adjustments to ensure optimal conditions throughout the production process. This level of precision is essential for maintaining the integrity of biopharmaceutical products.
- Facilitating efficient scaling: As biomanufacturing processes are scaled up, automation ensures that they can be scaled efficiently while minimizing costs. Automated systems provide the necessary precision and control to handle the complexities of large-scale production.
Top 6 Automation Solutions
In 2024, biomanufacturing professionals continue to look increasingly for automation solutions that can help them achieve their goals of reducing manufacturing costs and enhancing manufacturing efficiency — two of the top priorities in the industry today. Some relevant and impactful automations in the biomanufacturing industry include:
- Multivariate data analysis, which helps in understanding complex process interactions and predicting outcomes, leading to more precise control of bioprocesses.
- Robotics that can perform repetitive tasks such as sampling, media preparation, and cell culture maintenance, increasing throughput and reducing human error.
- AI-driven predictive maintenance systems that can forecast equipment failures before they occur, minimizing downtime and ensuring smooth operations.
- Digital twins, which are virtual replicas of bioprocesses that allow for simulation and testing of different scenarios without disrupting actual production. This technology can help optimize processes and troubleshoot issues in a risk-free environment.
- Smart bioreactors equipped with smart sensors can monitor and transmit real-time data on process conditions, enabling remote control and optimization.
- 3D printing can be used to quickly produce custom components for bioreactors, enabling rapid prototyping and adjustments to meet specific process needs.
Key Takeaways
The biomanufacturing industry is undergoing significant changes, driven by evolving demands for efficiency, cost reduction, and sustainability. One of the most prominent shifts is the increasing emphasis on lower-cost SUS and automation.
Both technologies are expected to help resolve pressing challenges in biomanufacturing, particularly staffing shortages. SUS are designed for ease of installation and can be discarded after use, so they can significantly reduce the need for specialized personnel to manage complex cleaning and validation processes. Similarly, automated systems handle intricate production tasks with precision, minimizing the reliance on highly skilled operators. This can become a major factor as innovative, complex platforms like cell therapies advance. Together, SUS automation can enable facilities to implement and operate with fewer expert staff, addressing a growing concern in the biomanufacturing sector where the demand for skilled labor is outpacing supply.
References:
- Langer, E.S., et al., Report and Survey of Biopharmaceutical Manufacturing Capacity and Production, 21st annual edition, BioPlan Associates, Rockville, MD, July 2024, 506 pages.
- International Society for Pharmaceutical Engineering (ISPE) launch of the ISPE Community of Practice (CoP) on Sustainability Accessed 2 Sept 2024: https://ispe.org/news/ispe-announces-sustainability-community-practice
About The Author:
 Ioanna Deni is a BioPlan market researcher scientist experienced in quantitative market research analysis. She is completing her Ph.D. in biomedical sciences and has extensive experience in biopharmaceutical life science research. Her research background includes quantitative and qualitative market research expertise as an AI and healthcare specialist. Reach her at info@bioplanassociates.com or 301-921-5979.
Ioanna Deni is a BioPlan market researcher scientist experienced in quantitative market research analysis. She is completing her Ph.D. in biomedical sciences and has extensive experience in biopharmaceutical life science research. Her research background includes quantitative and qualitative market research expertise as an AI and healthcare specialist. Reach her at info@bioplanassociates.com or 301-921-5979.
