Assessing And Navigating Testing For Parenteral Packaging And Delivery Systems: Performance Testing
By Jennifer Riter

As combination products evolve, new and complex interactions among packaging components and delivery systems have arisen. For pharmaceutical manufacturers, it is critical to understand the compatibility and performance of the primary packaging system with both the drug product and the delivery systems for successful development of the drug product. Applying a systematic approach and strategy for component and system qualification is critical to ensure drug product quality, safety and efficacy. System performance is critical in understanding suitability. It becomes more challenging to consider performance when a drug product is combined with a delivery system such as a pen injector; which would then be considered and reviewed as a combination product. Another common combination product is a pre-filled syringe system.
It is important to consider the drug product and device functionality early in the development process. In addition, as containment system, delivery system, or combination product, are refined through development, device functionality must be continually evaluated.
There are many aspects to consider when developing a sound approach to performance testing to qualify packaging and delivery systems, and combination products. These include assessing performance risks, establishing the testing strategy, and executing the testing plan. In assessing the performance risks, it is important to start with identifying knowledge gaps and fully understanding product risks, and potential risks to the patient. Identifying and assessing risks can help set the foundation for the product testing strategy. A widely accepted tool to facilitate and capture information to assess risks is failure mode effects analysis, or FMEA. To further add to understanding product risks and help to formulate a testing strategy, Failure Cause Mapping is a very useful technique. Still another tool is an Ishikawa chart, which can holistically consider all possible risks based on simple perceived risks, past testing history, field failure reports, and manufacturing yield related data (e.g., in-line quality inspection systems data). All this information can drive actions for testing strategy input.
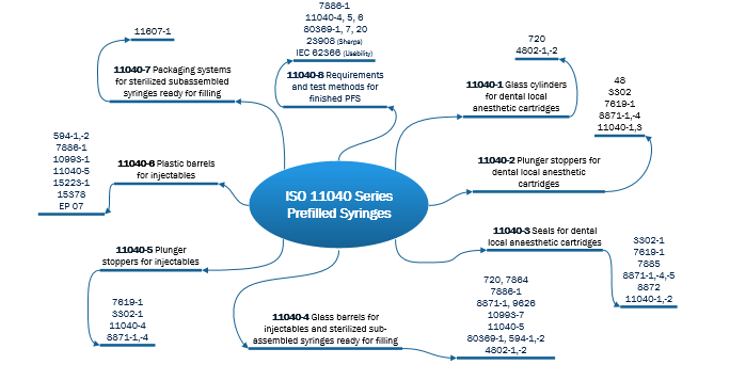
After assessing and understanding the performance risks, the next step is to establish the testing strategy. This step is an output of risk assessments, but also receives input from guidances from ISO, PDA, FDA, USP, and others. Rather than invent a testing strategy independently, it should be developed with input from widely accepted standards and guidances. A pre-filled syringe is an example where assessment of performance-based risks was used to establish the testing strategy. Understanding and using ISO resources, and creating an ISO reference library, is very important in creating the overall testing strategy. Figure 1 presents ISO resources for syringes from the 11040 Prefilled Syringe series. Within this series there are multiple standards with many additional standards outlined in the standards.
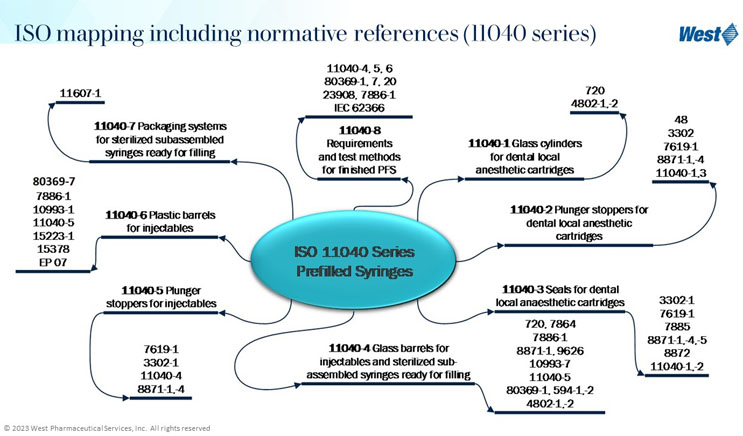
Figure 1. ISO 11040 Prefilled Syringes Standards
These standards and references are very helpful in identifying widely accepted testing methodologies, which are important in formulating the testing strategy. For example, the 11040-4 Glass Barrels for Injectables has normative references ISO 7864 Sterile Hypodermic Needles for Single Use Requirements and Test Methods, and ISO 7886-1 Sterile Hypodermic Syringes for Single Use.
A testing strategy created with guidance from widely accepted ISO standards, for example, brings an inherent benefit – long term continuity between past and future data sets. Additionally, time will be saved in method and product testing verification when widely accepted standards-based methods are created at the outset; as performance-related data will be better understood and transferable. It is not until completion of the steps of assessing the performance risks and establishing the testing strategy, based on that risk assessment, that the testing plan can be executed to assess the performance of the system.

For more information on West’s prefillable syringes, click here.
